Are you fascinated by the ability to control your home's temperature, lighting, and appliances with a simple tap on your phone? The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly transforming our world, and at its core lies the power of remote control.
Smart home devices are just the beginning. IoT devices, equipped with sensors, software, and networking capabilities, are collecting and sharing data at an unprecedented scale. This data is then harnessed to provide insights, automate tasks, and optimize processes across various sectors. The ability to manage these devices remotely is not just a convenience; it is a necessity for efficiency, security, and innovation. This article dives deep into the world of remote IoT device management, exploring its applications, benefits, and the challenges that come with it.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Remote IoT device management refers to the ability to control, monitor, and manage Internet of Things devices from a distance, typically using a network connection. |
| Key Functions | Includes tasks like device registration, health monitoring, firmware updates, configuration changes, and data collection. |
| Benefits | Enhanced operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, reduced downtime, improved security, and remote troubleshooting. |
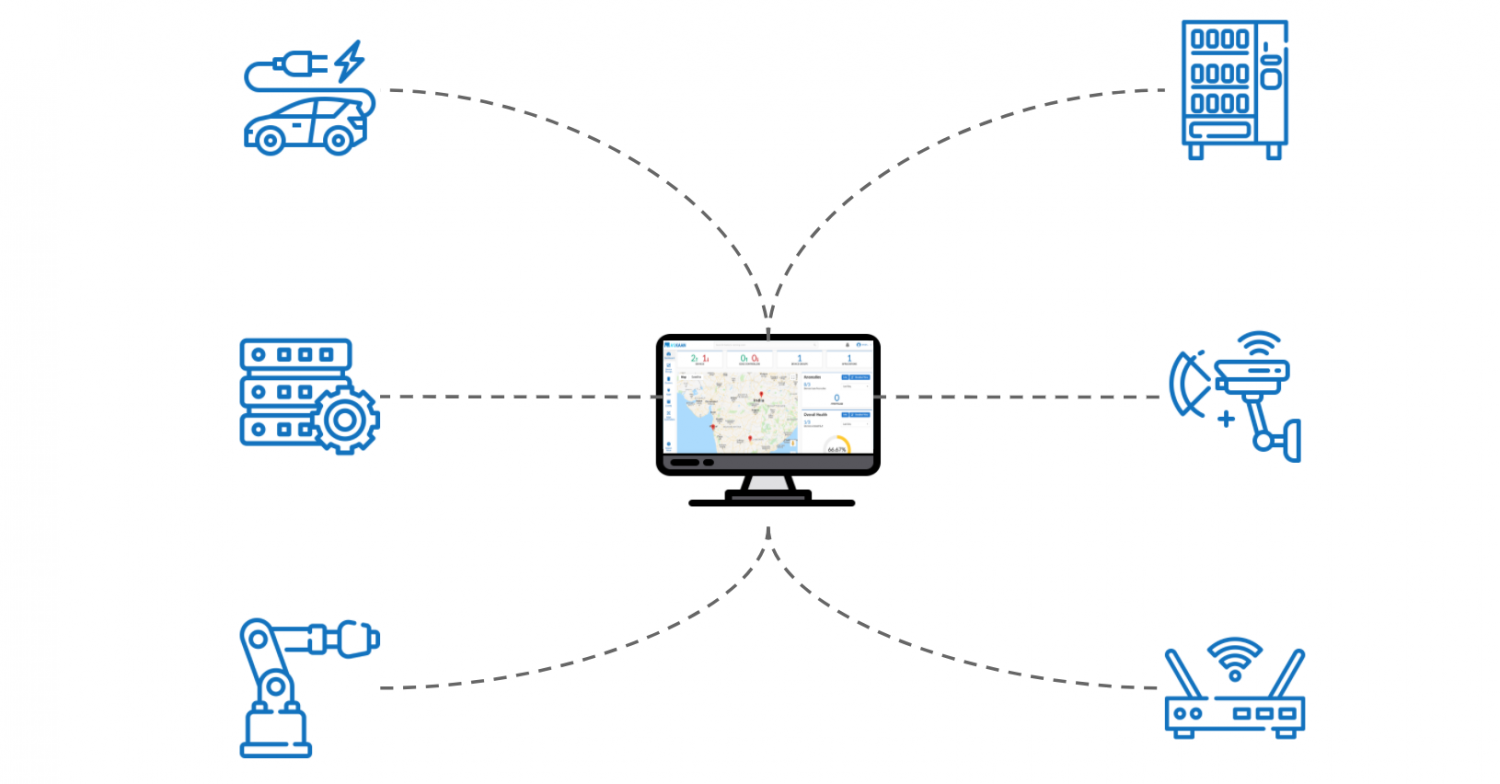
| Use Cases | Smart homes (thermostats, lights), industrial automation, agriculture (soil monitoring), healthcare (remote patient monitoring), and supply chain management. |
| Technologies Used | Cloud platforms (AWS IoT, Azure IoT), communication protocols (MQTT, CoAP), security protocols (SSL/TLS), and device management platforms. |
| Challenges | Security vulnerabilities, network connectivity issues, device diversity, scalability concerns, and data privacy considerations. |
| Future Trends | Edge computing, AI-powered device management, increased automation, and more sophisticated security measures. |
The core functionality lies in the ability to implement effective command structures. This involves designing the right set of instructions that the devices can understand and execute. These commands need to be robust, reliable, and secure, as they are the gateway through which users interact with their devices. The successful design and implementation of these command structures determine the ability of devices to perform their intended functions reliably and securely, from adjusting a smart thermostat to monitoring the health of industrial machinery.
One of the major advantages is the power of scheduled automation. Setting up schedules allows devices to perform tasks automatically, freeing up valuable time and resources. For instance, smart lights can be programmed to turn on and off at specific times, or irrigation systems in agriculture can automatically water crops based on soil moisture levels and weather forecasts. Scheduled automation not only enhances convenience but also optimizes energy consumption and resource allocation, leading to significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency. These automated schedules are pivotal in establishing the full potential of IoT devices, making them more efficient and intelligent.
Remote IoT device management goes beyond individual device control; it fundamentally changes how we approach various sectors. In agriculture, for example, IoT devices monitor soil conditions and crop growth, ensuring optimal irrigation and resource management. In the manufacturing industry, the integration of IoT and advanced technologies is transforming operations, from robotic automation to predictive maintenance. These technologies enable businesses to anticipate equipment failures, optimize performance, and ultimately increase their bottom line. Remote functionality enables seamless monitoring, evaluation, and manipulation of trends related to these devices.
Managing IoT devices at scale brings its own set of complexities. A unified platform that streamlines this process is crucial for effective management. This often includes a suite of tools for device registration, configuration, and ongoing monitoring. The AWS IoT Device Management unit, for instance, is designed to facilitate the easy integration and management of devices already utilizing AWS services. Furthermore, compatibility with various platforms streamlines device management, providing a unified and intuitive user experience.
The integration of people, processes, and technology with connectable devices and sensors is essential to enable the remote monitoring, status assessment, and manipulation of these devices. Peter T. Lewis, during a 1985 speech at the Congressional Black Caucus Foundation, defined the Internet of Things. In the context of IoT, remote functionality plays a vital role in connecting devices and systems from a distance, allowing users to access, monitor, and manage applications and processes. This level of remote control is not merely about efficiency but also about ensuring the safety and security of operations, from maintaining equipment to preventing potential dangers.
The fundamental tasks of an IoT gateway device management system include integrating new devices into the network, monitoring their ongoing health, and ensuring uptime. This is a critical step in IoT management. Web dashboards provide an easy way to visualize and control these remotely managed devices. The definition of IoT is evolving, leading to objects that interact and communicate with one another, offering us opportunities to be more efficient in how we manage our resources.
Fog computing has emerged as a promising solution to enhance the quality of service by bringing cloud resources closer to the terminal devices. By offloading tasks to nearby "fogs", we can achieve faster processing and responsiveness. This is especially important for time-sensitive applications. With the growing number of connected devices, the demand for 5G networks is also increasing, creating new capabilities for the Internet of Things.
The term "Internet of Things" has become increasingly broad, representing a paradigm shift in how we interact with our environment. Several IoT products have surpassed the number of humans on this planet, and the trend is only set to continue. This growth introduces a need for efficient, effective device management solutions. From smart homes to industrial applications, the need to control and manage devices from a remote location is crucial.
| Key Concepts | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote Access | The ability to control and monitor IoT devices from a distance via a network connection. |
| Device Management Platform | A software system designed to manage and control IoT devices, including registration, monitoring, and configuration. |
| Scheduled Automation | The pre-programmed execution of tasks at specific times or intervals. |
| Command Structures | The design and implementation of instructions that IoT devices can understand and execute. |
| Security Protocols | Measures and technologies used to secure data transmission and device access, such as SSL/TLS. |
| Edge Computing | Processing data closer to the devices at the network's edge to improve responsiveness and reduce latency. |
| Fog Computing | A distributed computing infrastructure that brings cloud resources closer to devices, improving quality of service. |
One example of remote access solution is SocketXP, a cloud-based IoT remote access and device management solution providing SSH access to devices behind NAT routers or firewalls over the internet. This technology underscores the critical nature of secure remote access and the ongoing evolution of these crucial technologies.
The article is a summary of the basic concepts of the IoT integration platform for remote task management. These smart devices connect to the internet, enabling users to control and monitor tasks remotely. Remote IoT device management is an essential step that will keep your business safe and secure, and will help it grow. In the competitive IoT market, effective management is essential for tailoring business requirements. With the right tools and strategies, you can manage your devices to ensure their efficiency.
.jpg)
Detail Author:
- Name : Oda Schimmel DDS
- Username : gaylord.verna
- Email : vgrady@oberbrunner.com
- Birthdate : 1984-02-12
- Address : 5391 Collier Branch New Gabrielburgh, CO 01427-1004
- Phone : +1-831-606-2882
- Company : Mosciski-Bergstrom
- Job : Telephone Station Installer and Repairer
- Bio : Officia adipisci quisquam numquam praesentium fuga quod. Voluptate aperiam et et enim voluptatum sunt perspiciatis. Sed quae velit eos voluptas consectetur pariatur est quo.
Socials
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@ewiza
- username : ewiza
- bio : Ducimus quia non explicabo debitis. Voluptatem nulla aut ullam adipisci est.
- followers : 5362
- following : 990
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/emilewiza
- username : emilewiza
- bio : Ducimus rerum rerum saepe qui quas.
- followers : 141
- following : 2785
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/emile.wiza
- username : emile.wiza
- bio : Earum id quasi iusto aut earum animi ipsam.
- followers : 1092
- following : 2097