Can the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices truly be harnessed without exposing them to significant security vulnerabilities? The answer hinges on how effectively we secure remote connections, and p2p (peer-to-peer) download methods, coupled with technologies like SSH (Secure Shell), offer a promising, albeit complex, solution. The rapid expansion of IoT, from smart home appliances to industrial sensors, has created a massive attack surface, and securing these devices is paramount to preventing data breaches and system compromises.
The integration of IoT devices into our daily lives has grown exponentially, presenting both unparalleled opportunities and significant challenges. The convenience and efficiency offered by these interconnected devices are undeniable; however, their increasing reliance on remote connections introduces a critical vulnerability point. Traditional security protocols, often designed for static networks, struggle to cope with the dynamic nature and distributed architecture of many IoT deployments. This is where innovative solutions, like secure p2p downloads, become vital. The core problem is not just connecting, but doing so safely and without exposing devices to unnecessary risks. As technology continues to evolve, so must our security practices.
Let's delve into the specific scenarios and tools. This article will unravel the nuances of securely connecting remote IoT devices utilizing p2p download techniques. Moreover, we will explore the implementation of SSH and the selection of tools. The security challenges associated with remote device connections are significant, particularly as the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand. The need for secure and reliable connections grows exponentially with each technological advance. Within today's interconnected world, IoT devices play a crucial role in simplifying daily tasks and improving productivity. Below, you'll find essential information.
- Delucas Tragic Greys Anatomy Journey Death A Recap
- Perfect Medium Steak Internal Temperature Guide Tips
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Concept: P2P Download Security | This revolves around establishing a secure, direct connection between a remote IoT device and a source for file transfers, like software updates or configuration changes, bypassing traditional, potentially vulnerable, centralized servers. This direct connection can be facilitated through various methods but relies on robust encryption and authentication to safeguard data during transit. |
| Role of SSH in IoT Security | SSH, a protocol for secure remote login and command execution, plays a critical role in securing IoT devices. It offers a secure channel for administrators to manage and configure the devices remotely. SSH uses encryption to protect all data transmitted between the device and the management server, providing a secure way to interact with the device. Using SSH for file transfers is a secure option, and SSH key-based authentication further enhances security by removing the need for passwords. |
| Why P2P SSH is Ideal for IoT Devices | Combining p2p with SSH creates a powerful, secure remote access system. P2P allows devices to connect directly, reducing reliance on intermediary servers that could be vulnerable. SSH provides the secure channel for communication. This setup is particularly well-suited for IoT because:
|
| Setting Up SSH on macOS for IoT Devices | Setting up SSH on a macOS device intended for use with an IoT device involves several steps:
|
| Free SSH Tools for macOS Users | macOS comes with built-in tools for SSH:
|
| Securing IoT Devices with P2P SSH: Best Practices | Implementing robust security practices is crucial when using p2p SSH:
|
| Best Practices for Remote IoT Connections (General) | Beyond SSH, general security best practices for remote IoT connections include:
|
| The Future of IoT Security | The future of IoT security is likely to involve:
|
The process of establishing secure p2p connections, particularly involving SSH, presents unique challenges. Understanding the specific vulnerabilities of both SSH and the inherent risks associated with p2p file sharing is crucial. While these approaches can enhance security, they can also inadvertently introduce new attack vectors if not carefully implemented. For example, insecurely configured SSH servers can be easily exploited, while malicious actors might attempt to inject malware during p2p file transfers.
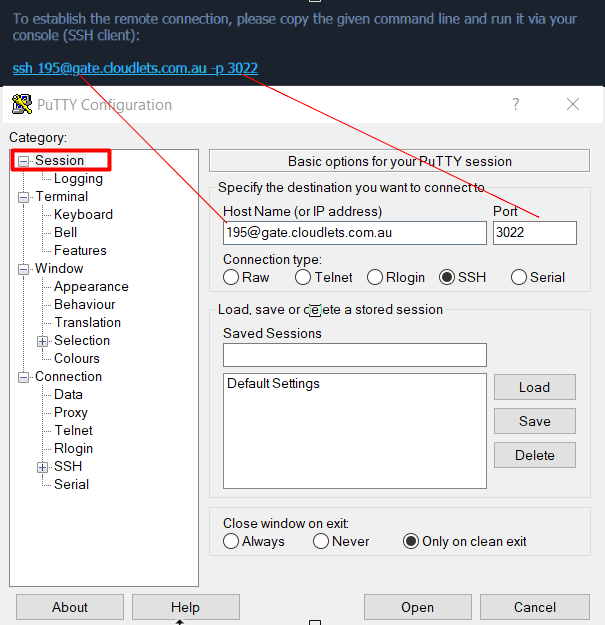
Consider the practical steps involved in setting up such a system. The initial setup involves configuring the IoT device, which might be a resource-constrained Raspberry Pi or a more complex industrial controller. This will necessitate the installation and configuration of SSH, including generating and distributing the appropriate SSH keys. The challenges extend beyond the technical. For instance, in scenarios where the IoT device is behind a NAT (Network Address Translation) router or firewall, the process becomes more complex. The use of SSH tunneling, port forwarding, and possibly even VPNs, may be necessary to establish a direct, secure connection.
Beyond the technical aspects, the legal and ethical implications of securing remote IoT connections should be taken into consideration. Issues such as data privacy, compliance with regulatory requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), and the responsible use of technology need to be addressed. Furthermore, the potential impact on user privacy, especially in smart home or wearable devices, should be carefully evaluated. Transparency and user consent are key considerations when dealing with any technology that collects or transmits data.
- Bianca Censori Age Career Facts About Kanyes Wife Unveiled
- Boost Writing Confidence Discover Wewillwrite Today
When selecting an SSH tool for macOS, several factors should be considered. The built-in Terminal application, with its `ssh` and `scp` commands, provides a basic, secure foundation. It's often the starting point for many users due to its simplicity and pre-installed nature. For those seeking more features, such as graphical interfaces and advanced scripting capabilities, third-party options are available. However, the core functionality of SSH, including key management, encryption, and secure file transfer, is generally well-supported by the standard macOS tools.
The concept of "securely connect remote iot p2p download" suggests a direct, encrypted communication channel between the IoT device and a remote system. This approach contrasts with more conventional methods that rely on cloud-based intermediaries, which can introduce single points of failure or vulnerability. P2P SSH, therefore, represents a robust solution, especially when dealing with potentially sensitive data or environments where reliability is a top priority. The combination of encryption and authentication, inherent to SSH, makes this approach inherently secure. Remember, the level of security is directly proportional to the expertise of the implementor.
Troubleshooting such a setup can involve several considerations. First, verifying that the SSH server is running correctly on the IoT device is a fundamental step. This involves checking the service status and ensuring that the SSH port (typically port 22) is open and accessible. Then, the correct configuration of firewall rules on both the IoT device and the connecting machine is essential. Incorrectly configured rules can block the SSH connection. Furthermore, key-based authentication is a frequent source of issues; making sure the public key is properly added to the IoT device's authorized keys is critical.
The convergence of IoT with other technologies presents both advantages and new threats. The integration of 5G, for example, offers faster and more reliable wireless communication, which facilitates remote management and control of IoT devices. The adoption of edge computing shifts some processing from the cloud to the device itself, potentially reducing latency and increasing security, but this shift introduces new security challenges. The integration of AI and machine learning enhances data analysis and automates threat detection, but also raises concerns about data privacy and the potential for bias in algorithms.
The evolving IoT landscape is rapidly changing. The convergence of these technologies makes securing remote IoT connections increasingly complicated. By focusing on best practices, choosing the right tools, and staying informed of the latest security developments, professionals and enthusiasts alike can mitigate risks and protect their valuable data and systems.

Detail Author:
- Name : Miss Amely Hudson
- Username : riley02
- Email : estel.boyle@keeling.com
- Birthdate : 2000-06-06
- Address : 166 Dickens Parkway Apt. 317 Port Rhianna, UT 01049-0794
- Phone : 657.973.9228
- Company : Johnston-Kautzer
- Job : Forensic Science Technician
- Bio : Corporis voluptates molestiae quo iste. Pariatur saepe aut id eos asperiores vel sit. Aliquid mollitia vero sed voluptates dolor earum.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/vonruedena
- username : vonruedena
- bio : Ea sunt esse unde consequuntur quaerat numquam.
- followers : 3052
- following : 2801
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@adalbertovonrueden
- username : adalbertovonrueden
- bio : Et animi quaerat vel in atque tempora qui.
- followers : 6988
- following : 21
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/vonruedena
- username : vonruedena
- bio : Quos mollitia temporibus odio. Dolorem suscipit similique iure est id omnis. Voluptatum recusandae aut expedita quia consequatur.
- followers : 3338
- following : 1213
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/adalbertovonrueden
- username : adalbertovonrueden
- bio : Molestias mollitia non cum beatae a. Rerum fugit amet commodi quia.
- followers : 883
- following : 1593